Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory

Which part(s) of the brain, when impaired by alcohol, play an important role in memory: This is a very important question. And today we are going to explore Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory:
Effects of Alcohol on the brain:
- All the brain activities down (GABA, glutamate)
- Dopamine UP
- Serotonin UP

As far as the point is concerned about the effects of alcohol on the brain, alcohol, or more specifically ethanol affects the several functions of the human brain. I want to mention here that if you are drinking alcohol for the relief of your brain. That in this way your brain would have a sigh of peace then you are paving the very wrong way.
Alcohol does not only affect the brain but it affects almost every function in the human body and disturbed them.
Regarding the domain of Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory: Alcohol is commonly known as a DEPRESSANT of the central nervous system.
The diverging about this particular thing is that it inhibits all the brain functions, causing a range of physiological effects such as impaired body movements and absurdity speech. After drinking alcohol, you would be out of your senses.
You would be not knowing that what are you doing and what are you speaking. Moreover, there is a huge possibility you can reveal all of your secrets in front of the gathering with whom you drunk.
This is pretty ominous for the person who has drunk. You will also speak the secrets that you don’t want to tell any other person. It can ruin all your reputation.
The pleasurable feeling associated with drinking, on the other side of the mirror, is linked to alcohol-induced dopamine release in the brain’s reward pathway.
Additionally, alcohol also increases levels of brain serotonin, a neurotransmitter implicated in mood regulation. As we know that, the brain is a complex network of a plethora of neurons. Neurons can be excitatory or inhibitory.
If we would talk about excitatory neurons, they stimulate others to respond and transmit all the electrical messages. On the contrary, inhibitory neurons SUPPRESS responsiveness, preventing excessive firing.
Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory:
Now after describing all the effects of alcohol on brains function, we will unwrap our today’s focal topic on Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory:
Hippocampus is the main part of the human brain which plays an important role in order to responsible for memory. Hippocampus is responsible for both short- and long-term memory of the human brain.
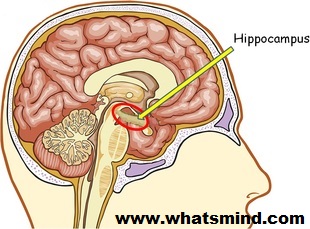
When you drink one or two times, it damaged the functions of the brain. Most of this process occurs in Hippocampus.
The devastating point about this particular thing is that there are a lot of disadvantages of drinking alcohol which not only affect your body functions but also affect yours very badly on your daily routine.
Like, alcohol can reduce your decision-making capacity that you would not be able to make professional decisions very consciously. In this way, it can damage your practical life.
You would be shocked that every year 95000 people die in the United States of America because of alcohol. And 5.3% all over the globe. You can say that 1 of every 20 deaths is due to the excessive use of alcohol.
Last about Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory: The vital reason behind this range of deaths is the side effects of alcohol. There is no doubt in it that alcohol reduces stress and anxiety but in the same way, it is also very fatal for human life. Alcohol causes the most common diseases like cancer, heart attack, dementia, stomach disorder, and a long consumption of alcohol causes impaired of the body parts.
For more content like Which part(s) of the brain when impaired by alcohol play an important role in memory: visit www.whatsmind.com
For more information, contact us at Gmail




